Subsidiary books II
R57.50
Use, by you or one client, in a single end product which end users are not charged for. The total price includes the item price and a buyer fee.
Resource Description
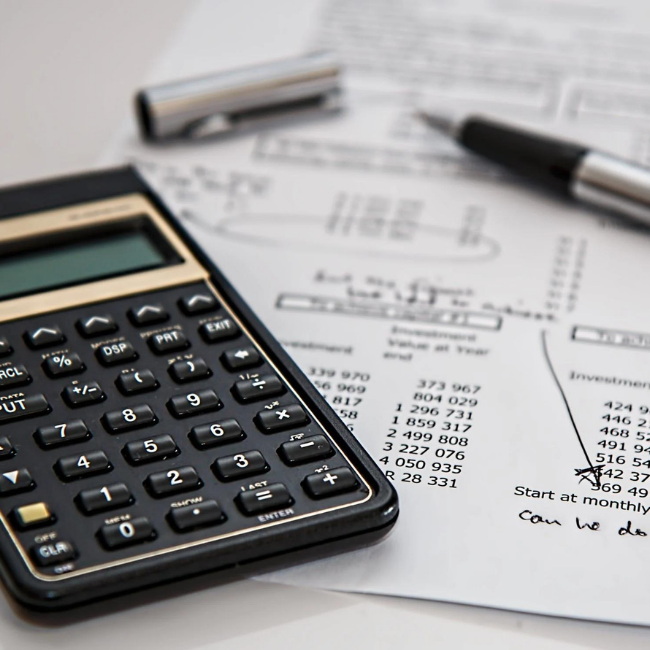
In this Unit, we are going to discuss in detail about sales book, sales returns book, bills payable book, bills receivable book and journal proper.
Sales book is a subsidiary book which is maintained to record credit sale of goods. Goods mean the items in which the business is dealing. These are meant for regular sale.
Sales returns book is a subsidiary book, in which, details of return of goods sold for which cash is not immediately paid are recorded
Bills receivable book Also known as a B/R book, bills receivable book is a subsidiary or secondary book of accounting, where all bills of exchange, which are receivable for the business, are recorded. The total value of all the bills receivable for an accounting period is transferred to the books of accounts
Bills Payable Book Also known as a B/P book, bills payable book is a subsidiary or secondary book of accounting where all bills of exchange, which are payable by the business, are recorded. The total value of all the bills payable for an accounting period is transferred to the books of accounts.
Journal proper is a residuary book which contains record of transactions, which do not find a place in the subsidiary books such as cash book, purchases book, sales book, purchases returns book, sales returns book, bills receivable book and bills payable book. Thus, journal proper or general journal is a book in which the residual transactions which cannot be entered in any of the sub divisions of journal are entered. Detailed discussion for bill of exchange along with it’s features as well as difference between bills receivable and bills payable and also bills receivable and accounts receivable is made for the clear understanding of the various concepts.



 KES(KSh)
KES(KSh) USD($)
USD($) GBP(£)
GBP(£) GHS(₵)
GHS(₵) NGN(₦)
NGN(₦) MUR(₨)
MUR(₨) BWP(P)
BWP(P) AUD($)
AUD($) TZS(Sh)
TZS(Sh) INR(₹)
INR(₹) PHP(₱)
PHP(₱) AED(د.إ)
AED(د.إ)






