Subsidiary books – 1
R46.00
Use, by you or one client, in a single end product which end users are not charged for. The total price includes the item price and a buyer fee.
Resource Description
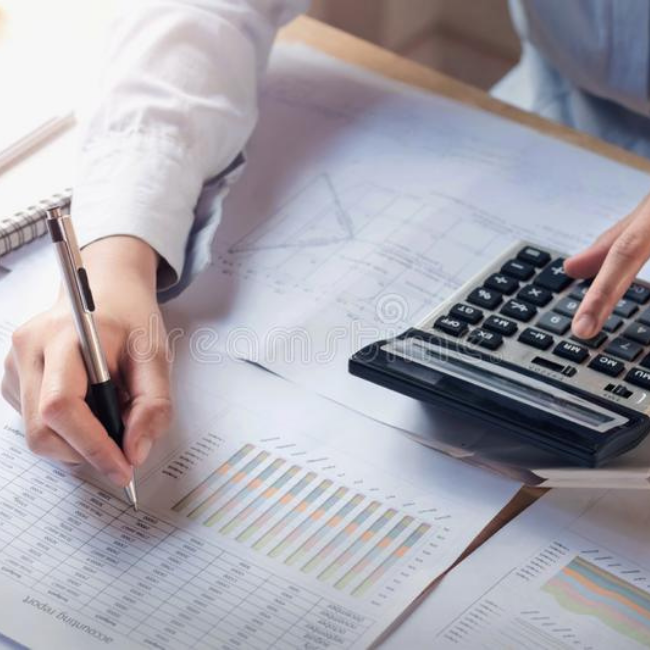
Subsidiary books are sub-divisions of journal in which transactions of similar nature are recorded. These are the books of prime entry. Instead of recording in one journal the transactions are recorded in a number of prescribed books.
Types of Subsidiary books:
The number of subsidiary books may vary according to the requirements of each business. Based on the nature of business and the volume of transactions the following subsidiary books are usually maintained:
1. Cash book: Cash book is a book of prime entry that records all transactions made by a business in both cash and a bank instrument.
2. Purchase book: It keeps a record of only transactions relating to credit purchase of goods.
3. Sales book: It keeps a record of only credit sale of goods.
4. Purchase returns book: Also known as returns outward book, a purchase returns book is prepared to record goods returned by a business to its suppliers.
5. Sales returns book: Also known as returns inward book, a sales return book is prepared to record goods returned to a business by the customers.
6. Journal Proper : A book in which all miscellaneous transactions which are not recorded in any other subsidiary book is called a journal proper.
7. Bills receivable book: It is a book that records all bills receivable to a business, the total of bills receivable book is posted on the debit side of the B/R account.
8. Bills payable book: is one of the subsidiary books that records all bills payable by a business, the total of bills payable book is posted on the credit side of the B/P account.
In this Unit, Purpose of subsidiary books, it’s uses and features are also discussed along with the meaning for cash discount and trade discount and the difference between the two.
The detailed explanation for the purchase book and purchase returns book is also given with an example.



 KES(KSh)
KES(KSh) USD($)
USD($) GBP(£)
GBP(£) GHS(₵)
GHS(₵) NGN(₦)
NGN(₦) MUR(₨)
MUR(₨) BWP(P)
BWP(P) AUD($)
AUD($) TZS(Sh)
TZS(Sh) INR(₹)
INR(₹) PHP(₱)
PHP(₱) AED(د.إ)
AED(د.إ)






