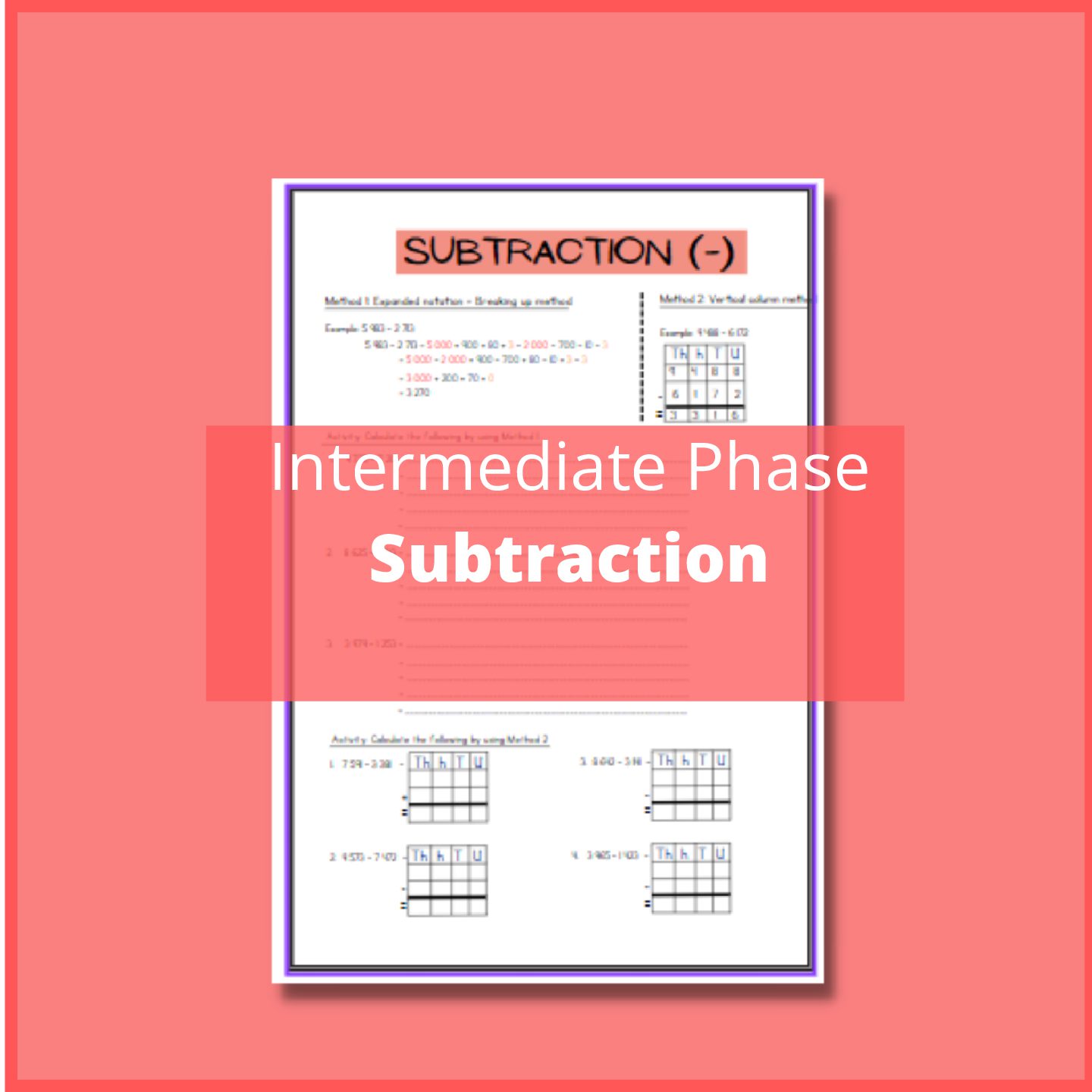
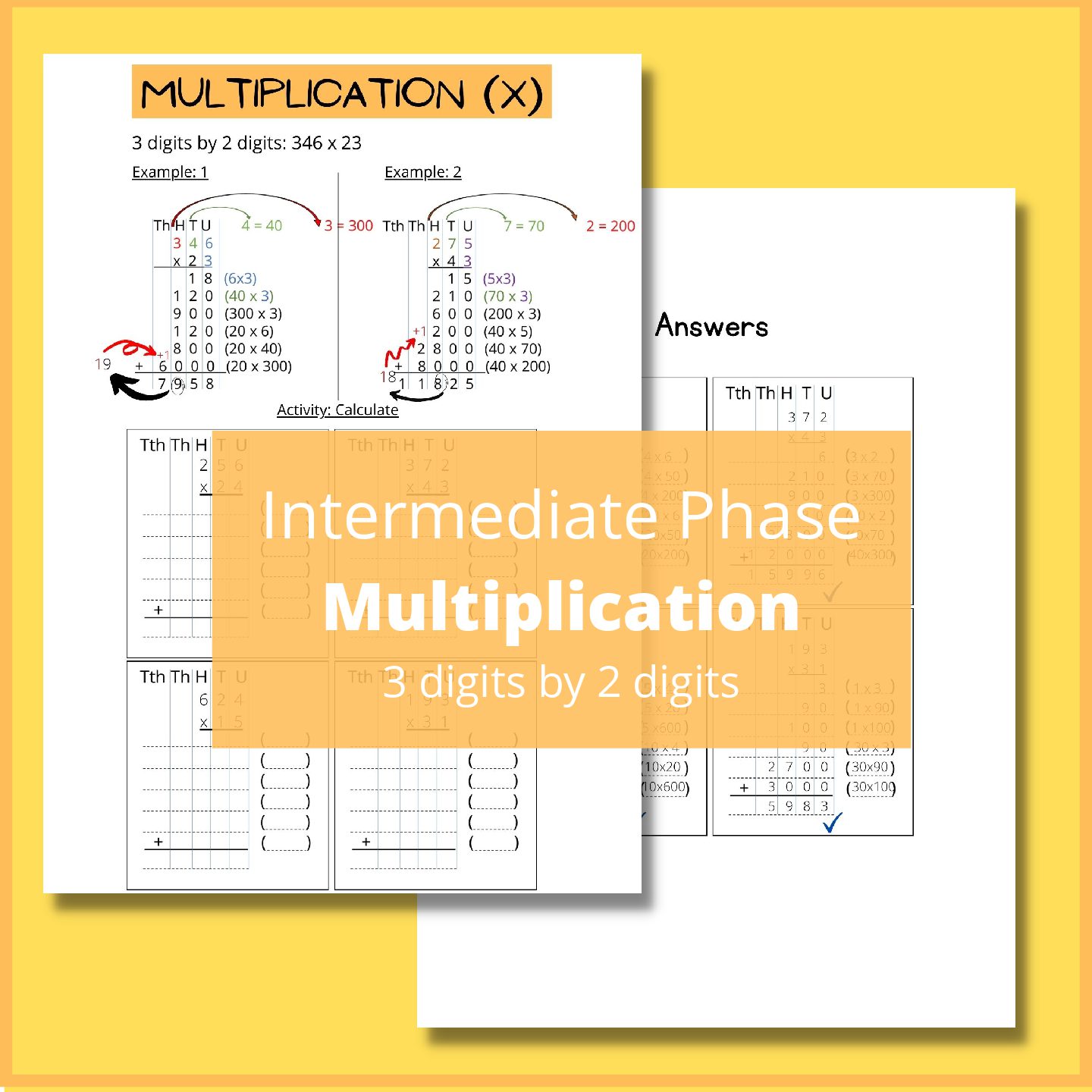
Grade 7 Technology Project Term 3 – Task 3
R86.25
Use, by you or one client, in a single end product which end users are not charged for. The total price includes the item price and a buyer fee.
Resource Description
Task Overview:
Students are tasked with designing and constructing a model crane using simple materials like popsicle sticks, string, tape, and possibly a few other basic supplies. The project typically involves several stages:
- Research and Design (2D Drawings):
- Students begin by researching different types of cranes and their functionalities.
- They then create initial sketches or 2D drawings of their crane design. This includes planning the structure, dimensions, and mechanisms (e.g., pulleys, levers) they intend to incorporate.
- Prototype Construction:
- Using their 2D drawings as a guide, students build a prototype of their crane using the provided materials. This phase encourages problem-solving and creativity as they translate their designs into a physical model.
- Testing and Iteration:
- After constructing the prototype, students test their crane to see how well it performs its intended functions (e.g., lifting a small load).
- Based on their tests, they may need to make adjustments or improvements to their design to enhance functionality or stability.
- Documentation (3D Drawings):
- Students document their final design through 3D drawings or models. This can be done using software tools if available, or manually with detailed illustrations that show the crane from multiple angles.
- These drawings should include annotations that explain key features of the crane, such as how the pulley system works or how different parts connect.
Learning Objectives:
- Engineering Principles: Understanding basic mechanical principles such as leverage, force, and stability.
- Design Thinking: Learning to iterate on designs based on testing and feedback.
- Technical Drawing: Developing skills in creating accurate 2D and 3D representations of objects.
- Teamwork and Communication: Collaborating with peers, sharing ideas, and presenting findings.
Assessment Criteria:
- Functionality: Does the crane perform its intended task effectively?
- Design Creativity: How innovative and well-thought-out is the design?
- Documentation: Clarity and completeness of the 2D and 3D drawings.
- Problem-Solving: Ability to identify and address challenges encountered during the construction and testing phases.
- Presentation: Quality of oral and visual presentation when sharing their project with classmates.
Conclusion:
This project not only teaches practical engineering skills but also encourages creativity, critical thinking, and teamwork. By combining hands-on construction with technical drawing, students gain a holistic understanding of the design process from conception to execution.



 KES(KSh)
KES(KSh) USD($)
USD($) GBP(£)
GBP(£) GHS(₵)
GHS(₵) NGN(₦)
NGN(₦) MUR(₨)
MUR(₨) BWP(P)
BWP(P) AUD($)
AUD($) TZS(Sh)
TZS(Sh) INR(₹)
INR(₹) PHP(₱)
PHP(₱) AED(د.إ)
AED(د.إ)