Accounting Equation Method with Illustrations
R46.00
Use, by you or one client, in a single end product which end users are not charged for. The total price includes the item price and a buyer fee.
Resource Description
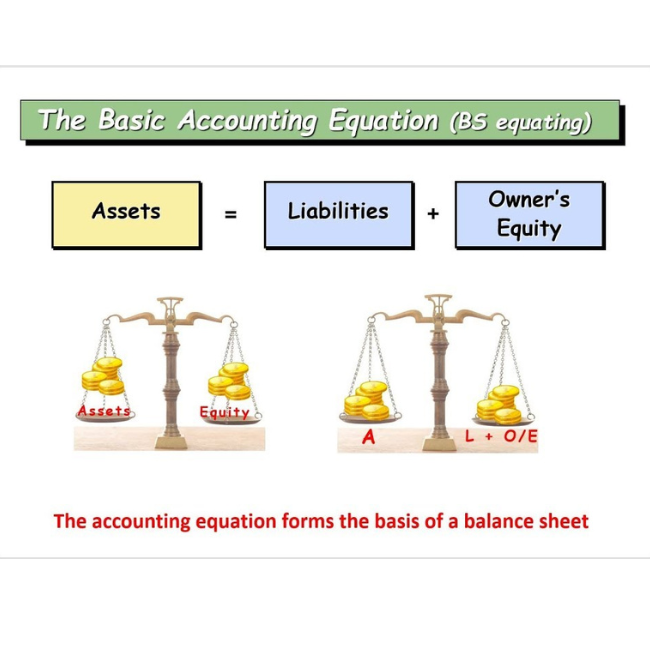
The relationship of assets with that of liabilities to outsiders and to owners in the equation form is known as accounting equation.
Under the double entry system of book keeping, every transaction has two fold effect, which causes the changes in assets and liabilities or capital in such a way that an accounting equation is completed and equated.
Capital + Liabilities = Assets
(or)
Assets = Liabilities + Capital + Revenues – Expenses
Recording of transactions as per accounting equation approach is explained below with the help of a transaction:
Analyze the effect of each transaction on assets and liabilities and show that the both sides of Accounting Equation
(A = L + C) remains equal :
(i) Introduced Rs 8,00,000 as cash and Rs 50,000 by stock
Assets = Liabilities + Capital
Cash + stock = Liabilities + capital
————————————————————————-
8,00,000 + 50,000 = 0 + 8,50,000
————————————————————-
Effects: (i) cash comes in → Increase in assets
(ii) stock comes in → Increase in assets
(iii) Capital provided by the owner → Increase in capital of business
In this Unit, solving of an accounting equation with many transactions have been explained with detailed analysis.



 KES(KSh)
KES(KSh) USD($)
USD($) GBP(£)
GBP(£) GHS(₵)
GHS(₵) NGN(₦)
NGN(₦) MUR(₨)
MUR(₨) BWP(P)
BWP(P) AUD($)
AUD($) TZS(Sh)
TZS(Sh) INR(₹)
INR(₹) PHP(₱)
PHP(₱) AED(د.إ)
AED(د.إ)